An opportunity to increase the amount of performance feedback on your team
Peer feedback is frequently given via indirect surveys, perhaps as part of a 360-degree feedback program. I would like to argue that this doesn’t really count as peer feedback, since it is time-delayed, indirect, and frequently non-actionable. I’m more in favor of direct peer feedback, since it is specific and immediate, can be focused on improving performance and teamwork. However, there are some reasons to be wary direct peer feedback, as I detail in my previous post.
However, the main reason I’m in favor of direct peer feedback is that it multiplies the amount of performance feedback that team members receive. Let me explain:
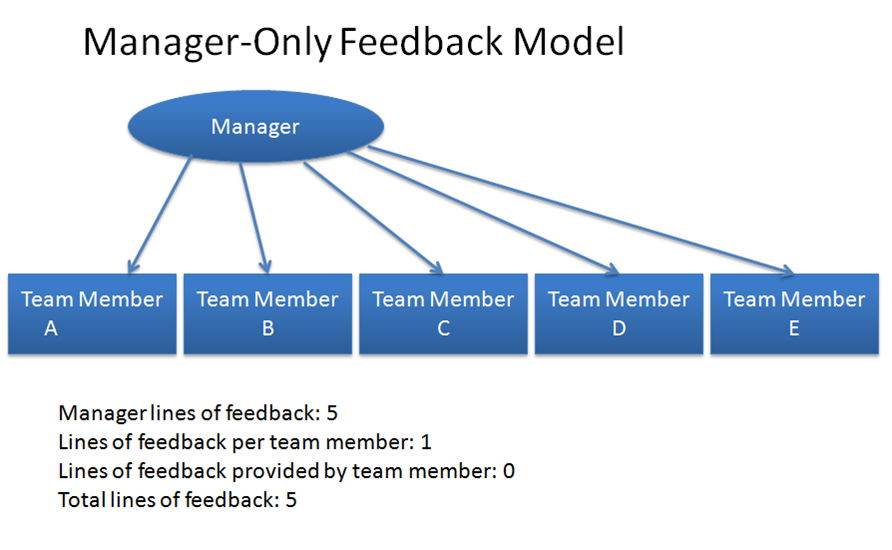
A traditional model for how employees improve their performance is through manager observation, and then the manager provides coaching and corrective feedback. For a team of five people, this is what it looks like:
Look familiar? This is the popular conception for how employees receive feedback on their performance. It is predicated on the belief that the manager has enough expertise in all the areas of the team performance to provide feedback, and the manager actually has the skill to provide feedback, which, alas, is not always the case. When most of us start a job, this is the general mental model that we have. After all, the manager is the one who evaluates our performance, and knows the expectations for performance! Employees expect to receive feedback from the manager on performance.
Some pros and cons of peer feedback directly given by peers
I’ve written articles lately about the risks of peer feedback from surveys and how peer feedback can be best utilized to improve performance on your team and in your organization. A frequent scenario is that the manager receives some sort of report with “360 feedback” from peers on team members’ performance. Then the implication is that the manager has to do something about it.
When the feedback comes from a survey, the feedback is indirect, and it’s of lower quality. The feedback is coming from a secondary source, there is also a serious time delay, the facts of the matter are usually murky and there is no alternative course of action offered. It’s also not clear if the person receiving the feedback actually did the wrong thing. Really, as far as feedback to improve performance is concerned, it’s kind of useless.
But what about the scenario when a peer gives feedback directly to another peer? Is this desirable?
For example, lets say you are working on a project and a peer consistently misses a deadline. The peer says, “You have missed the deadlines, and this is causing project delays. Is there a way you correct this?” That counts as peer feedback, and it isn’t waiting for a survey process.
Here are some reasons peer feedback directly given can be desirable:
–The feedback is more likely to be specific and immediately given
–The feedback is likely to have an alternate course of action
–The feedback is likely to comes from an expert on policies and best practices
–The feedback is not directly tainted by managerial power relations related to promotions and annual review toxicity
–The feedback is likely aimed at immediately improving performance of both the individual and the team
These are all excellent arguments in favor of peer feedback directly given, but there is another argument in favor of direct peer feedback.
New publishing schedule for Manager by Design
Starting February 28, 2011, Manager by Design is moving to a once a week publishing schedule, with new articles appearing every Monday morning. We’ve published twice a week since the start of Manager by Design in 2009, amassing tons of great tips on people and team management – if you haven’t checked the back articles lately, now’s the time!
You can still look forward to more great articles on management and the emerging field of Management Design. Thanks to all for reading Manager by Design!
How to use peer feedback from surveys for good (it’s not easy) – Part 2
This article is the second in a series on how managers can better use peer “feedback” from surveys. In general, a manager should be dubious about the quality of feedback that information provided on peer feedback surveys, since they are non-specific and time delayed. At best, this information provides clues and subtext for what is actually happening, and don’t reach the bar of performance feedback, but instead is general info. In the previous article, I discussed how managers should
- Treat the info as clues
- Stick to directly observed behaviors
- Ask for specific and immediate feedback from peers (instead of waiting for the survey to come around)
Today, I’d like to focus on using this information that the survey provides to understand the greater system that is driving the performance of your employees.
4. Use peer feedback as a basis for a strategy session with your employee
I’ve written before about how when giving performance feedback, isn’t always about the individual performance of an employee. Many times, peer feedback can reveal these systemic challenges with the job.
How to use peer feedback from surveys for good (it’s not easy) – Part 1
I’ve been writing a lot about peer feedback lately. What’s interesting is that peer feedback is often about the subtext of what happened between the peer and the employee. The manager looks deeply into the peer feedback to identify the hidden meaning of what the peer was getting at. But what about the thing above the subtext, the thing right there on the surface? What’s that called?
The text.
(Thanks to Whit Stillman’s Barcelona for help writing the opening of this article)
In this case, the text is the actual employee behavior, and this provides a clue for how managers should use peer feedback.
1. Treat peer feedback as clues, hidden meanings and shadowy innuendo
If you get a peer feedback report (often the result of some sort of “360 degree survey” conducted by the HR department), understand that this is a series of random snapshots into an employee’s behavior. Treat it as such. When the peer feedback says, “Jeremy is the greatest!” that means something good, but we’re not really sure. When the peer feedback says, “Jenny does so much to make this a strong team.” There’s something there about teamwork. It’s interesting, but we don’t really know what that means. When the peer feedback says, “Anthony never does any work.” This means that someone somewhere objects to Anthony’s performance. We’re not sure to what exactly this is referring, but there is something there, we think.
In other words, it is all unverified information, but it might give you some clues to something, or maybe not.
Examples of how peer feedback from surveys is misused by managers
In my previous post, I describe how peer feedback from 360 degree surveys is not really feedback at all. At best, it can be considered, “general input from peers about an employee.” Alas, it is called peer feedback, and as such, it risks being misused by managers. Let’s talk about these misuses:
As a proxy for direct observations: Peer feedback is so seductive because it sounds like something that can replace what a manager is supposed to be doing as a manager. One job of the manager is to provide feedback on job performance and coach the employee to better performance. However, with peer feedback from surveys, you get this proxy for that job expectation: The peers do it via peer feedback. Even better, it is usually performed by the Human Resources department, which sends out the survey, compiles it, and gives it to the manager. Now all the manager has to do is provide that feedback to the employee. See, the manager has given feedback to the employee on job performance. Done!
Never mind that this feedback doesn’t qualify as performance feedback, may-or-may not be job related, or may-or-may not be accurate.
The incident that sticks and replicates: Let’s say in August an employee, Jacqueline, was out on vacation for three weeks. During that time, a request from the team Admin came out to provide the asset number of the computer, but Jacqueline didn’t reply to this. And worse, Jacqueline didn’t reply to it after returning from vacation, figuring that the admin would have followed up on the gaps that remained on the asset list. Then it comes back a year later on Jacqueline’s peer feedback that the she is unresponsive, difficult to get a hold of and doesn’t follow procedures. This came from the trusted Admin source!
Why peer feedback from surveys doesn’t qualify as feedback
In a previous post, I identified peer feedback from 360 degree surveys as a source of inputs where a manager gets information about an employee’s performance. Peer feedback via 360 degree surveys has become increasingly popular as a way of identifying the better performers from the lesser performers. After all, teams should identify people who get great peer feedback, and do something about the team members who get poor peer feedback. The better the peer feedback, the better the employee, right? Well, maybe. Maybe not. Let’s talk about how peer feedback should be used, and not misused.
OK, peer feedback. As Demetri Martin would say, “This is a very important subject.”
First of all, by definition, peer feedback on surveys is, from the manager’s perspective, indirect reporting of an employee’s performance. The peer gives the feedback via some intermediary source (survey, email request, or, if requested, verbal discussion), and then that information gets interpreted as to what it means by the manager, or perhaps even some third party algorithm.
So it is essentially hearsay. Since it is one degree away from direct observation of performance, peer feedback is inherently more risky to use as a way to provide feedback on an employee’s performance. Here’s why:
The best feedback – or the most artful, as I like to say – has the following qualities, amongst others:
–It is specific
–It is immediate
–It is behavior-based
–It provides an alternative behavior
Let’s see how peer feedback stands up!
Specificity: Peer feedback on surveys comes in the form of a summary of behaviors over an aggregate period of time. Sample peer feedback will say something like, “John is always on top of everything, which I enjoy,” or “John needs to stop checking messages during the team meeting.” Now here’s the rub: This looks like general feedback, but it may be (you don’t know for sure) related to one incident. The “on top of everything” may refer to arranging a co-worker’s birthday party. The “check messages during a meeting” may have happened during the one meeting when his daughter was undergoing surgery. Or it could be something that John always does. You don’t know. It’s general or it’s specific. You don’t know.
Or. . .have you ever seen this kind of peer feedback?
“During the September 18 team meeting, John was checking his messages when he should have been working with the team to brainstorm solutions to resolving the budget shortfall. Then, on the September 25 team meeting, John received two phone calls during the meeting, interrupting the discussion flow about what our strategy for next year should be. Then, on October 2, John. . .”
This kind of peer feedback doesn’t happen on surveys. Instead, you get summaries of behaviors that may be based on a specific incident. . . or not. It may be work-related, or not. You don’t really know.
More reasons the big boss’s feedback on an employee is useless
Perhaps I’m obsessing about this scenario too much, but I just can’t get out of my head the damage that managers of managers cause when they start assessing employees not directly reporting to them. I call this “tagging” an employee.
In a previous post, I describe the moment where a “big boss” (the employee’s manager’s manager) meets with an employee (or even just hears something about an employee or sees a snapshot of the employee’s work) and provides an assessment of the employee. “That employee really knows what she’s doing!” “That employee doesn’t seem to have his head in it.”
The problem? There are many:
–It rates the employee on behaviors not directly related to doing the job, but it’s based on an abstracted conversation about the work or a limited impression of the employee.
–It puts the manager in the middle in a situation where it would seem appropriate to correct the employee, even when it is inappropriate.
I describe what the manager ought to do about this here. But I’m still obsessed with the peculiar angst that this kind of indirect feedback will create in the employee – even when the “feedback” is good. So before I dive into my obsession, my advice to the managers of managers out there: Don’t provide assessments on an employee. Keep it to yourself. If you are really into assessing an employee’s value, you have to do the work of direct observation of work performance.
Now, let’s look at this “feedback” from the employee’s perspective and the damage it causes in an organization:
When a big boss starts trying to identify the top performers and the bottom performers based on their limited interactions, here is a survey of the damage it causes:
Makes employees one-dimensional: The employee immediately transforms from a multi-talented, hard-working, problem-solving contributor to whatever the “tag” is. This is bad even if the tag is good! If the tag is “hard working”, it diminishes the problem-solving, multi-talented part. It also creates a cloud around what the employee does the whole time at work, and instead puts a simplistic view of the employee’s value.
Assumes that the employee is like that all the time: Similarly, if the employee does a particular thing that gets the big boss’s notice, then that is the thing that the employee has to live up to or live down. For example, if the employee does a great presentation, that is what the employee is seen as being good at – the presentation, and the employee is expected to be presenting all the time to have value. There’s no visibility into the teamwork, project management, collaboration, technical insights, or creativity that went into the presentation. Just the presentation. Then if the person is not presenting all the time, then perhaps they are slacking off? That’s what the big boss might think!
What a manager can do if the big boss puts a tag on an employee
In my previous post, I described a common scenario and the mess it makes:
An employee meets with the big boss (the manager’s manager) in what is often called a “skip level” one-on-one. Or the big boss sees – or hears about — some output of an employee, representing a small fraction of the employee’s output. The big boss then makes a judgment on the employee – what I call a “tag” on the employee. That tag now sticks on the employee. It creates a big mess that puts the manager in a bind – how do you address this employee’s tag?
Here are tips for what the manager caught in the middle can do to handle the tag – whether good or bad.
1. Keep the tag in mind and wait for observed behaviors that are consistent with “the tag”
Ok, if the manager’s manager (“big boss”) is so keen at identifying employee’s essence and value, then surely there will be plenty of opportunities to observe directly the performance of the employee that has earned that tag. Whether the tag is “negative attitude” or “rock star”, the manager needs to wait for opportunities to see behaviors that fit with this tag, and correct those behaviors.
If the manager is keeping a performance log on the employee, these trends should manifest if they are correct, and fail to appear should they be incorrect.
2. Ignore what your manager says and do your job of managing
Almost the same as the point above, but subtly different. It doesn’t matter what the boss’s boss says. If you are managing your employee, work with your employee to make sure he meets performance expectations, provide feedback that drives to the desired behaviors, then, if the employee is performing the job duties according to expectations, then it kind of doesn’t matter what the boss’s boss says. Your assessment is based on better data and you can justify it.
What to do when your boss gives feedback on your employee? That’s a tough one, so let’s try to unwind this mess.
Here’s the scenario:
Your employee meets with your boss for a “skip level” meeting. After the meeting, the employee’s boss’s boss (your boss) tells you what a sharp employee you have.
Or, let’s say that your boss tells you that your employee needs to “change his attitude” and “has concerns about your employee.” This is very direct feedback about the employee, and it comes from an excellent authority (your boss), and if you disagree with it, you disagree with your boss.
But this information is entirely suspect. Whether the feedback from the “big boss” is positive or negative, the only thing it reveals is how the employee performed during the meeting with the boss. And unless your employee’s job duty is to meet with your boss, it actually has nothing to do with the expected performance on the job. So if the feedback is negative, do you spend time trying to correct your employee’s behavior during the time the employee meets with the big boss, when it isn’t related to the employee’s job duties?
In addition, the big boss often prides him or herself on the ability to cut through things and come to conclusions quickly, succinctly, and immediately. The big boss will come to a conclusion about the employee based on the data provided in the one-on-one meeting, and will expect this conclusion to be corroborated by you and everyone else.
The big boss, in this process, will put a tag on the employee, whatever it is. Here are some examples of tags:
Up-and-comer
Introverted
Not a go-getter
Whip-smart
Not aware of the issues
Could be a problem
. . .or, the dreaded, ambiguous, “I’m not sure about him.”
What’s worse, since the “tag” originated with the big boss, it will likely stick.